The past year has seen an explosion in AI-powered search experiences, with ChatGPT emerging as the clear leader among large language models (LLMs) directing traffic to online retailers. But does this traffic convert? Not quite yet. According to a major new study, ChatGPT is gaining ground in e-commerce referrals, but Google’s organic and paid search channels still dominate when it comes to actual sales and revenue.
The data paints a clear picture: while AI assistants like ChatGPT are making inroads, they are not about to dethrone Google. Yet.
LLMs Drive Traffic, But Not Yet Sales
Researchers analysed 12 months of first-party data from 973 e-commerce sites, covering more than 10 billion sessions and $20 billion in revenue. They compared over 50,000 ChatGPT-originating transactions against 164 million from traditional channels including search, social, email, and affiliates.
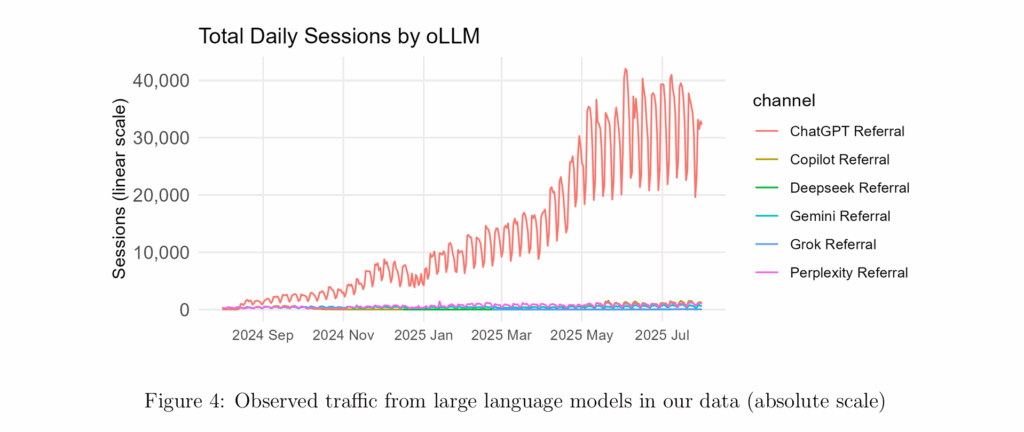
The topline result? ChatGPT referral traffic accounted for just 0.2% of total sessions – around 200 times less than Google organic search. And while it is the overwhelming leader among LLMs (driving over 90% of AI referral traffic), ChatGPT significantly underperforms when it comes to conversion metrics.
Conversion Rates Tell the Story
In terms of conversion rate (CR), ChatGPT trails most major channels:
-
Affiliate traffic led the pack, with 86% higher conversion rates than ChatGPT
-
Email and organic search also outperformed ChatGPT, with organic delivering a 13% uplift in CR
-
Only paid social lagged behind, with ChatGPT converting 53% better than paid social in relative terms
So while ChatGPT traffic appears relevant, it rarely leads to a purchase on the first click.
Revenue Per Session Lags Too
When it comes to revenue per session (RPS), the picture remains consistent:
-
ChatGPT outperformed paid social, but that was the only win
-
Every other traditional channel – including organic and paid search, email, and referral – drove higher revenue per session
-
In regression models that account for sparsity and control for device, site, and month, ChatGPT came up short across the board on RPS
While bounce rates from ChatGPT traffic were lower than many channels (a sign that users are at least landing on relevant content), they still were not as strong as Google’s search channels.
Average Order Value Declining
Interestingly, while ChatGPT’s conversion rate and revenue per session improved steadily across the 12-month period, average order value (AOV) fell. In other words, ChatGPT traffic is slowly converting more often, but users are spending less when they do.
This diverging trend weakens the case for ChatGPT as a strong revenue-driving channel, at least in its current form.
Trust Gaps and Attribution Challenges
The study’s authors suggest an important behavioural nuance: ChatGPT users may still rely on traditional platforms like Google to verify information or finalise a purchase. That means Google, or another last-click channel, may get the credit even if ChatGPT played a role earlier in the journey.
In other words, AI-assisted discovery may be shaping customer journeys in invisible ways.
This is a limitation of last-click attribution, which the researchers acknowledge. As AI assistants become more integrated into the customer experience, marketers may need to revisit their attribution models to capture the full value of LLM engagement.
Projections Show Growth, But No Parity
Regression-based projections for the coming year show a positive trend. If current improvements hold, ChatGPT could close the conversion rate gap with organic search – but it will not catch up within the next 12 months. Revenue per session is also projected to rise, but again, not to the level of traditional channels.
The takeaway? AI search is gaining, but slowly. It is unlikely to disrupt Google Search’s dominance in the short term.
Why This Matters for Marketers
For senior marketers and e-commerce leads, the message is clear:
-
LLMs are emerging as a viable traffic source, but do not yet justify major investment as a primary conversion channel
-
AI discovery platforms like ChatGPT are still early-stage, with consumers often reverting to search engines before buying
-
Now is the time to test and learn. Brands that engage early and optimise for LLM visibility will be well-positioned as this channel matures
In short, while LLMs will not kill Google just yet, they are changing how customers discover products. And that matters.
What To Do Now
-
Start tracking LLM-driven traffic in your analytics stack. Use UTM parameters or custom campaign tagging to monitor performance
-
Optimise for LLM visibility by ensuring your product data, FAQs and structured content are indexable and high-quality
-
Watch conversion trends over time, especially for mobile-first users, where LLMs may offer greater convenience
-
Do not ignore attribution complexity. If your LLM traffic is not converting, ask whether it is influencing awareness or consideration earlier in the funnel
LLM Traffic is Not Yet a Google Killer
ChatGPT is becoming a serious player in e-commerce traffic. But in terms of conversion and revenue, it still lags well behind traditional digital marketing channels. Despite headlines forecasting an AI takeover, the data tells a more measured story.
Marketers should view LLM traffic not as a replacement for Google, but as a complementary layer in the modern discovery journey. The next year will be crucial in determining whether ChatGPT can move from curiosity to core channel.



RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
OpenAI Begins Testing Ads Inside ChatGPT
For the past two years, marketers have treated ChatGPT…
For the past two years, marketers have treated ChatGPT…
Google Rebuilds Checkout For AI Shopping
Agentic shopping has moved from theory to reality, and…
Agentic shopping has moved from theory to reality, and…
LinkedIn Reveals Jobs On The Rise 2026
LinkedIn has released its latest Jobs on the Rise…
LinkedIn has released its latest Jobs on the Rise…